RBI’s Current Repo Rate 2025: Insights You Should Know!

The RBI’s current repo rate presents a bigger picture narrating a strategic foresight. On June 6, 2025, the RBI announced a slashing of the repo rate to 5.50% in the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting. It means the repo rate went down by 50 basis points, highlighting the 3rd consecutive slash and a steep reduction since the beginning of 2020.
The policy repo rate reduced by 100 bps in a swift series since February 2025, showing limited space to support growth. This blog will take you through the current repo rate of RBI, what it is and more.
What Is Repo Rate? A Quick Snapshot
Repo rate is the rate at which the Central Bank of India i.e RBI lends money to commercial banks to balance the liquidity and fulfil the requirements of businesses.
The RBI repo rate is the most important policy interest rate in India. From time to time as part of the monetary policy review, RBI reviews the repo rate.
From the Central Bank of India Banks borrow money with a legal agreement. And the rate of interest charged by RBI is called the Repo Rate.
What is the Current Repo Rate of RBI?
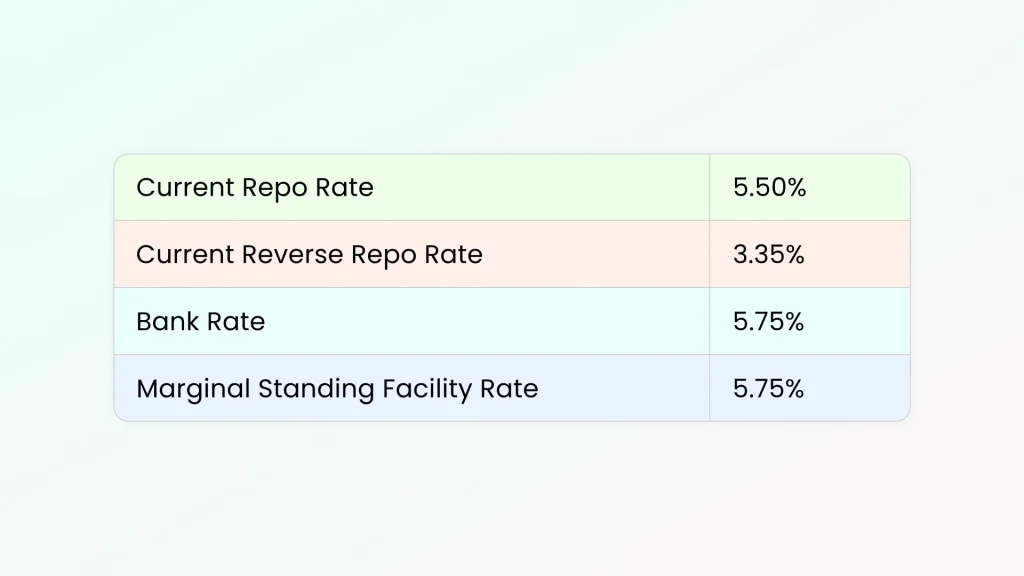
As of today, according to the June monetary policy agreement, the current repo rate is 5.50%, which was earlier 6%. This accounted for a reduction in repo rate by 50 basis points.
What is the Reverse Repo Rate in India? A Quick Takeaway!
The Reverse Repo Rate in India is referred to as the interest rate applied on the money borrowed by the RBI from commercial banks. It’s generally for a short period, and the RBI pays the interest to the banks.
What is the Current Reverse Repo Rate?
In India, the current reverse repo rate is 3.35% which remains unchanged.
A Quick Look Into RBI Repo Rates for July 2025!
History- From Current Repo Rate to November 2010!
| Date on Which Repo Rates Were Issued | Repo Rate |
|---|---|
| 6th June 2025 | 5.50% |
| 9th April 2025 | 6% |
| 7th February 2025 | 6.25% |
| 6th December 2024 | 6.50% |
| 9th October 2024 | 6.50% |
| 8th August 2024 | 6.50% |
| 7th June 2024 | 6.50% |
| 8th February 2024 | 6.50% |
| 8th December 2023 | 6.50% |
| 6th October 2023 | 6.50% |
| 10th August 2023 | 6.50% |
| 8th June 2023 | 6.50% |
| 6th April 2023 | 6.50% |
| 8th February 2023 | 6.50% |
| 7th December 2022 | 6.25% |
| 30th September 2022 | 5.90% |
| 5th August 2022 | 5.40% |
| 8th June 2022 | 4.90% |
| 4th May 2022 | 4.40% |
| 8th April 2022 | 4.00% |
| 10th February 2022 | 4.00% |
| 8th December 2021 | 4.00% |
| 8th October 2021 | 4.00% |
| 6th August 2021 | 4.00% |
| 4th June 2021 | 4.00% |
| 5th February 2021 | 4.00% |
| 4th December 2020 | 4.00% |
| 9th October 2020 | 4.00% |
| 6th August 2020 | 4.00% |
| 22nd May 2020 | 4.00% |
| 27th March 2020 | 4.40% |
| 6th February 2020 | 5.15% |
| 5th December 2019 | 5.15% |
| 4th October 2019 | 5.15% |
| 7th August 2019 | 5.40% |
| 6th June 2019 | 5.75% |
| 4th April 2019 | 6.00% |
| 7th February 2019 | 6.25% |
| 5th December 2018 | 6.50% |
| 5th October 2018 | 6.50% |
| 1st August 2018 | 6.50% |
| 6th June 2018 | 6.25% |
| 5th April 2018 | 6.00% |
| 7th February 2018 | 6.00% |
| 6th December 2017 | 6.00% |
| 4th October 2017 | 6.00% |
| 2nd August 2017 | 6.00% |
| 7th June 2017 | 6.25% |
| 6th April 2017 | 6.25% |
| 8th February 2017 | 6.25% |
| 7th December 2016 | 6.25% |
| 4th October 2016 | 6.25% |
| 9th August 2016 | 6.50% |
| 7th June 2016 | 6.50% |
| 5th April 2016 | 6.50% |
| 2nd February 2016 | 6.75% |
| 1st December 2015 | 6.75% |
| 29th September 2015 | 6.75% |
| 4th August 2015 | 7.25% |
| 2nd June 2015 | 7.25% |
| 7th April 2015 | 7.50% |
| 3rd February 2015 | 7.75% |
| 2nd December 2014 | 8.00% |
| 30th September 2014 | 8.00% |
| 5th August 2014 | 8.00% |
| 3rd June 2014 | 8.00% |
| 1st April 2014 | 8.00% |
| 18th December 2013 | 7.75% |
| 29th October 2013 | 7.75% |
| 20th September 2013 | 7.50% |
| 17th June 2013 | 7.25% |
| 3rd May 2013 | 7.25% |
| 19th March 2013 | 7.50% |
| 18th December 2012 | 8.00% |
| 30th October 2012 | 8.00% |
| 31st July 2012 | 7.00% |
| 18th June 2012 | 8.00% |
| 17th April 2012 | 8.00% |
| 17 March 2011 | 6.75% |
| 25 January 2011 | 6.50% |
| 02 November 2010 | 6.25% |
The Borrowing and Lending Dynamics
When banks face financial shortfalls, they turn to the central bank for assistance. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays this pivotal role. The rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks during financial crises is known as the “Repo Rate.” Commercial banks, in turn, borrow funds from the RBI by selling securities or bonds with an agreement to repurchase them at a predetermined price on a specified date.
Earning with Excess Funds
Conversely, when a commercial bank finds itself with excess funds, it can deposit these funds with the central bank and earn interest at the “Reverse Repo Rate.”Consider a commercial bank that deposits ₹10K with the RBI. Then, based on the current reverse repo rate, the RBI will pay interest of ₹335 to the commercial bank.
Current Repo Rate is 5.50%: How Does the Change Impact?
- It encourages the rise of borrowers through reduced EMIs for housing, automotive, personal, and MSME loans.
- The current repo rate roll-out witnessed a decline in fixed deposits and savings rates by 60-70 bps.
- It is likely to infuse liquidity, driving a rise in India’s GDP.
Repo Rate’s Impact on Liquidity
The Repo Rate holds significant sway over liquidity levels within the banking system. Should the RBI wish to increase liquidity, it will lower the Repo Rate, encouraging banks to sell their securities. Conversely, if the central bank seeks to control liquidity, it will raise the interest rate, dissuading banks from borrowing easily. A higher Repo Rate translates to increased interest earnings for the central bank from commercial banks, while a higher Reverse Repo Rate means that commercial banks earn a higher interest rate from the central bank.
Read More: NRI Account Types in India
How does RBI calculate the Repo Rate?
Ever wondered how the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) calculates the Repo Rate, a crucial determinant of a country’s monetary policy? Here’s a concise breakdown:
- Inflation Target: RBI sets a targeted inflation rate, often based on CPI or WPI, and uses the Repo Rate to maintain it within an acceptable range.
- Economic Growth: The Repo Rate influences economic growth; it can be adjusted to encourage or curb borrowing and spending depending on the economic scenario.
- Financial Stability: Ensuring the stability of the banking and financial sector is paramount, influencing the Repo Rate.
- Data Analysis and Expertise: RBI conducts comprehensive data analysis and consults experts to make informed Repo Rate decisions.
- Regular Review: The Repo Rate undergoes regular reviews and adjustments to align with the evolving economic landscape.
- Communication: RBI emphasizes transparency and clear communication regarding monetary policy decisions.
In essence, the Repo Rate’s calculation involves a delicate balance between controlling inflation, stimulating economic growth, ensuring financial stability, and fostering transparency, ultimately shaping the nation’s economic landscape by also making certain repo rate changes.
What is the Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate?
| Repo Rate | Reverse Repo Rate |
|---|---|
| RBI lends the money while commercial banks borrow it. | The Commercial banks lend the money while the RBI borrows it. |
| It bridges the temporary cash shortfalls | It minimises the overall circulation of money in economy |
| The interest rate is higher than the reverse repo rate | The interest rate is lower here |
| The current repo rate is 5.50% | The current reverse repo rate is 3.35% |
| The interest is applied through repurchase agreement | The interest is applied through reverse repurchase agreement |
Let’s Conclude
The RBI’s current repo rate slash to 5.50% is a tactical move to encourage borrowing and boost liquidity. Both repo and reverse repo empower businesses to make informed financial decisions that transform our country’s economic landscape.
Keep an eye on the monetary policies from the RBI and make a note as they continue to shape our GDP.
Stay tuned until we come up with the next update.
FAQs on Current Repo Rate
When was the current repo rate issued?
The current repo rate was issued on June 6 2025.
Who decides the repo rate?
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) decides the repo rate.
What is CLR and SLR?
- CLR is Cash Reserve Ratio which is sustained by commercial banks with RBI.
- SLR is a statutory liquidity ratio primarily maintained by commercial banks.
What is the reverse repo rate today?
Reverse repo rate today is 3.35%.






